- Why are there different types of HDMI connections?
- The different HDMI standards
- Connectors for all uses
- HDMI 1.4
- HDMI 2.0
- HDMI 2.1
- What types of HDMI cables to choose?
- Quality, length and price of HDMI cables
- Our selection of the best HDMI cables
- Conclusion
How do I choose the right HDMI cable? A simple question that too often leads to vague answers. HDMI 1.4, 2.0, 2.1 ... If you've ever connected an HDMI cable to your TV, PC monitor, or game console, and you've experienced display issues (see by display at all) , this guide is made for you.
Since their creation in 2002, HDMI cables have evolved a lot, and with them, the devices to which they are connected. We put everything together so that you are sure to make the right choice.

Why are there different types of HDMI connections?
Display sources and supported devices have evolved very rapidly. From “HD Ready” to “Full HD”, “4K” and other “8K”, the data flow has increased considerably, and with it HDMI connectors and cables.
A development so rapid that today we find many devices compatible with several HDMI standards.
It is therefore important to know the different HDMI connectors before choosing the compatible cables to connect your various devices, otherwise you will not be able to take full advantage of the visual and sound quality they can offer.
The HDMI standards that you should be concerned about today before purchasing a new product are: HDMI 1.4, HDMI 2.0, and HDMI 2.1. Let's see what they correspond to.
The different HDMI standards
We are talking here about the HDMI connectors on your TV, PC screen, Blu-Ray player, Box TV or even game console, and not cables that have other certifications on which we come back a little later in this article.
Connectors for all uses
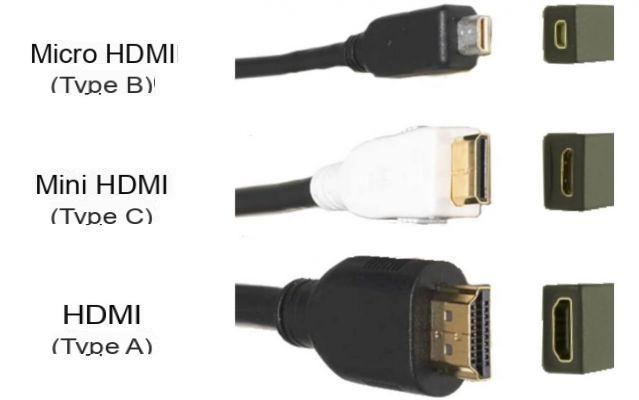
Before getting into the different HDMI standards, here is a reminder of the most common types of connectors. Note that their form will not change anything in terms of data transmission:
HDMI (Type A) : Game console, TV, TV box, Blu-Ray, Blu-Ray player.
Mini HDMI (Type C) : Tablets, Digital SLRs.
Micro HDMI (Type D) : Even smaller devices
 Read also:
Read also:
HDR10, HDR10 +, Dolby Vision: what are the differences between these technologies?
HDMI 1.4
Introduced in 2009, the HDMI 1.4 standard is the first to be able to support 4K 24FPS and UHD 30FPS display.
It is also compatible with 3D, but not with HDR10 or Dolby Vision because of its color space limited to 8-bit. We typically find this kind of port on the PS4, Xbox One S, as well as many TV screens.
HDMI 1.4 is also the first to introduce the HDMI Ethernet Channel (HEC) which allows connected compatible devices to share a wired internet connection, which can be very convenient for connected homes.
For example, if you have connected a Blu-Ray player and an HEC compatible TV, you will only have to connect one of the two devices to your box so that they both benefit from an Internet connection.
Please note: not all HDMI 1.4 cables are HEC compatible. This statement must appear on the product.
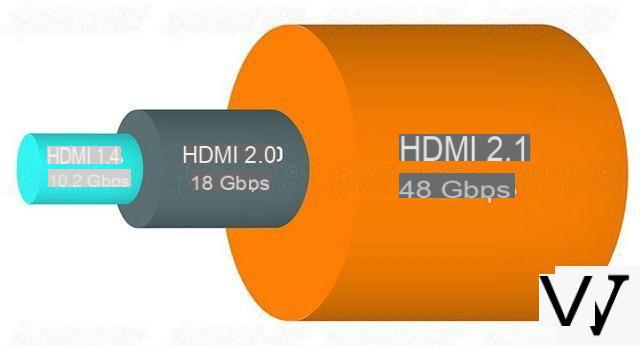
HDMI 2.0
The HDMI 2.0 standard allows an interesting upgrade with the support of 4K video streams up to 60 frames per second.
It also offers BT.2020 color space with up to 12-bit color depth, making it compatible with HDR10, HDR10 + and Dolby Vision technologies.
Sound is not left out with support for up to 32 audio channels at a high sample rate of 1536 kHz, as well as 4 audio streams and 2 video streams simultaneously.
HDMI 2.1
It is the most recent of the HDMI standards. It pushes the cursor even further by supporting 4K, 8K, 10K video streams and refresh rates of up to 120 FPS (with or without compression depending on the definition).
Like HDMI 2.0, version 2.1 is compatible with dynamic HDR found on HDR10 + and Dolby Vision technologies for a more immersive rendering of the different scenes.

HDMI 2.1 also provides a very low level of electromagnetic interference (low EMI) to prevent interference with nearby wireless devices.
HDMI 2.1 for gamers
The new HDMI standard also brings its share of novelties for moviegoers and gamers.
The PS5 and Xbox Serie X are for example equipped with HDMI 2.1 connectors and pride themselves on being able to run games up to 4K at 120 FPS.
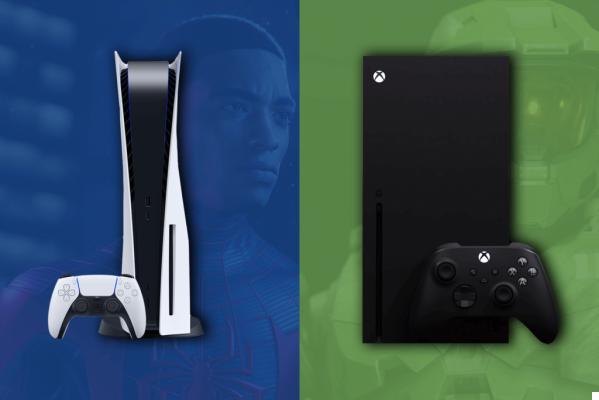

It will simply be necessary to ensure that your television set is also equipped with HDMI 2.1, and to use a certified cable “HDMI Ultra High Speed” able to manage a bandwidth up to 48 Gbps, to pass a large amount of data without compression.
Note: If you are wondering: yes, this type of cable is backwards compatible with HDMI connectors from previous generations.
We apologize in advance for the somewhat barbaric English terms that will follow, they are not always easy to translate.
Variable refresh rate
HDMI 2.1 takes advantage of VRR (Variable Refresh Rate) or “variable refresh rate” in Spanish. This technology can reduce or eliminate “lag”, “stuttering” and “frame tearing” (gamers will understand).
Auto Low Latency Mode
“Auto Low Latency Mode” (ALLM) as well as “Quick Frame Transport” (QFT) allow ideal latency level adjustment for a viewing experience without any lag to the image.
Other features of HDMI 2.1
The HDMI 2.1 standard never ceases to add “small” features which, when put end to end, make the difference when compared to the previous generation.
Quick Media Switching
“Quick Media Switching (QMS)” is an interesting feature that speeds up switching from one source to another. We have all already noticed this delay which can cause a black screen when we change the type of display. The QMS comes to settle this.
“HDMI Cable Power”
HDMI Cable Power is also a new feature in version 2.1. To understand it, you have to understand the difference between an active HDMI cable and a passive HDMI cable.
The passive HDMI cable is the one used by the general public. It does not need power to operate.
The active HDMI cable includes a built-in graphics processor as well as an additional USB cable that connects it to a power source. This type of cable amplifies the signal and improves image quality, especially on long cables over 3 meters.
The “HDMI Cable Power” function of the HDMI 2.1 standard thus makes it possible to benefit from the advantages of an active cable, without the need for external power supply via USB.

To use this feature, you will need a certified “HDMI Ultra High Speed” cable, as well as a source compatible with this technology (your TV for example). Enough to facilitate the installation of a “home cinema” or a video projector at home via a long cable, while enjoying optimal quality.
Regarding the eARC functionality with HDMI 2.1, we come back to it a little later in this file.
HDMI and CEC functionality
The CEC (Consumer Electronic Control) functionality of an HDMI device (whose connector is compatible) allows the user to control multiple devices with a single remote control.
A useful feature considering the proliferation of devices connected to each other, each with its own remote control.
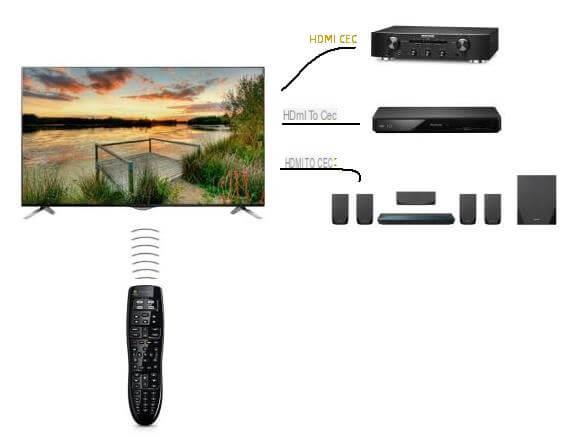

Huge potential for a feature little known to users. The HDMI 2.0 standard goes even further by offering the (theoretical) control of 15 devices simultaneously with a single remote control. Once again, all of your devices will need to be compatible with the CEC functionality.
HDMI and ARC functionality
The ARC (Audio Return Channel) functionality or “audio return channel” in Spanish allows sound return between two devices. Concretely, if your TV and your home cinema are compatible with the ARC function, only one compatible HDMI cable will be necessary to broadcast the audio and video signal.
You can do without the coaxial cable transferring audio signals from the TV to the home theater.

HDMI 2.1 eARC
The “Enhanced Audio Return Channel” (eARC) is an improvement of the ARC protocol, with which it is backward compatible.
It allows devices equipped with an eARC connector to be connected with a single HDMI cable. No more need to connect your console, or your internet box to your home cinema. Just plug them into your TV, and the HDMI cable from TV to home theater will take care of transmitting the audio signal.
EARC provides enhanced sound experience by streaming HD audio tracks, enabled by higher bandwidth that supports high-speed audio formats up to 192kHz, 24-bit, as well as 5.1 and 7.1 without compression.
Obviously, DTS-HD Master Audio, DTS: X, Dolby TrueHD and Dolby Atmos audio encodings are also supported.
To take advantage of HDMI 2.1 eARC, you will need an “HDMI High Speed Ethernet” cable or, again, an “HDMI Ultra High Speed” cable.
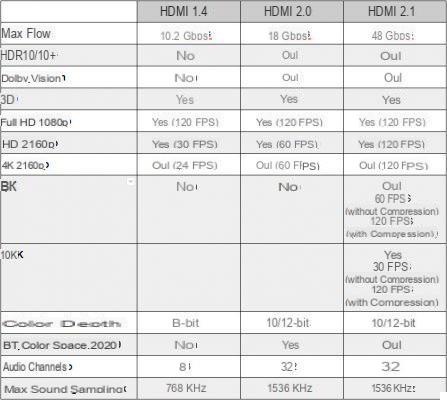
Summary of the different HDMI standards
For compatibility issues, it is essential to check the HDMI standards of your devices before purchasing a compatible cable. Here is a summary of the different HDMI standards and their technical characteristics:
To see in more detail what the HDMI 2.1 standard is capable of, you can also refer to the table below. It presents for each definition, the number of images per second supported, as well as the color space, the color depth, the bit rate and the speed.
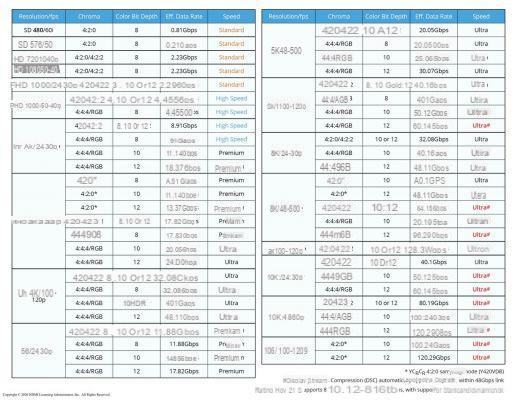 Click to enlarge.
Click to enlarge.
Note that the “Ultra” speed in red indicates automatic compression needed to keep the image and audio below the 48 Gbps mark supported by HDMI 2.1.
Now that you know everything about the HDMI standards that equip our electronic devices, it's time to choose the right HDMI cables to ensure optimal audio and video quality.
What types of HDMI cables to choose?
Today there are four certifications established by the HDMI Forum which is the official body behind the HDMI standard.
Each type of cable is classified according to its maximum overall speed and its capacity to pass the various audio and video streams.
These certifications are important to know to ensure that the HDMI cable you are going to purchase is compatible with the specifications of the HDMI connectors on your various devices.
HDMI cable certifications
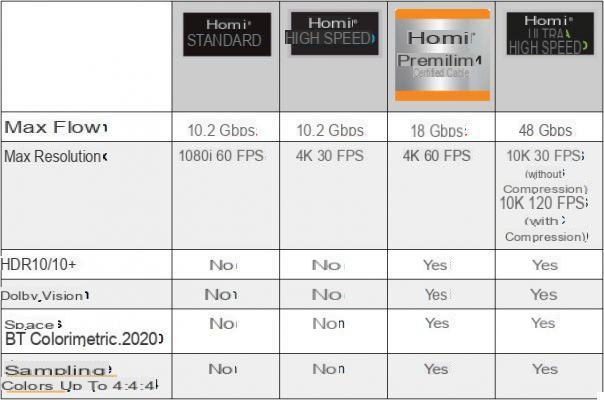
Note: Standard, High Speed and Premium High Speed HDMI cables have versions “with Ethernet” which indicate the presence of these cables of a channel dedicated to data transfer via the network.
Quality, length and price of HDMI cables
Now that you know what kind of cable you need, pay attention to their quality and functionality. Use common sense avoiding unusually inexpensive products compared to the competition and look at customer reviews.
Also pay attention to cables claiming to be compatible with ARC or CEC functions (see above in this section), which depend on the HDMI connector of the devices and not on the cables themselves.
In addition, a device can have multiple HDMI sockets, but only one of them is compatible with certain features like ARC.

Do not hesitate to ask questions directly to the seller. If you don't have an answer to your questions, it might be best to move on.
Any (quality) cables that are less than 5 meters should not be affected by a drop in speed. Beyond this (5, 8, 10 meters and more), you may notice flow attenuations, signal losses or even artefacts.
To avoid this, choose an HDMI fiber optic cable or an HDMI signal amplifier / repeater.
Our selection of the best HDMI cables
HDMI High Speed - 10,2 Gb/s jusqu'à 4K30FPS
-
HDMI Premium - 18 Gb/s jusqu'à 4K60FPS
- HDMI Ultra High speed - 48 Gb/s jusqu'à 8K60 FPS ou 4K120FPS
Conclusion
You now have all the weapons in hand to understand the HDMI standards of your devices and choose the right HDMI cable accordingly.
At the time of writing, the HDMI 2.0 standard is well established and allows you to comfortably enjoy 4K60 FPS images with the latest advances such as HDR or Dolby Vision.
Acquiring an HDMI cable with “Premium” certification is therefore the best option to benefit from a very good compatibility / price ratio.
The HDMI 2.1 standard and Ultra High Speed HDMI cables are clearly cut for the future, but will become strongly democratized in the months and years to come, driven by consumer equipment such as the PS5 and the Xbox Serie X, both equipped with this standard.